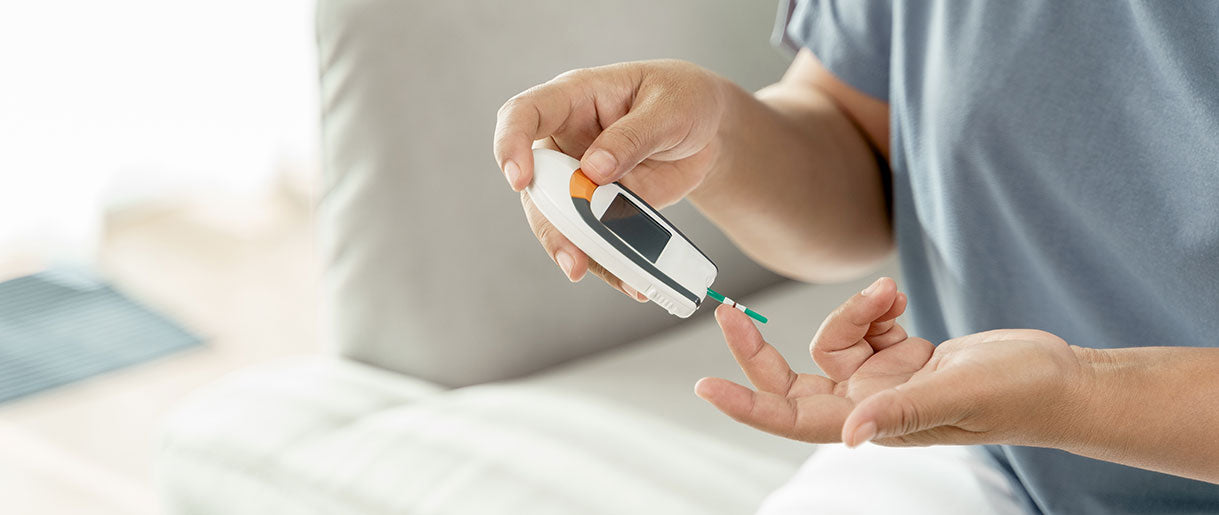
The first, and sometimes the most crucial, components of diabetes treatment include a healthy, balanced diet, exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. But if those are insufficient to keep your blood sugar levels stable, several supplements might be able to help.
Cordyceps mushroom has significant medical value due to the presence of unique types of sugar that may help treat diabetes. In addition, it has been demonstrated that the mushroom lowers blood sugar levels by acting similarly to insulin and has been found in numerous animal studies to lower blood sugar levels.
So, let’s explore the link between Cordyceps and diabetes. Below, we will talk about cordyceps diabetes benefits and how to utilize the mushroom to keep your blood sugar levels down.
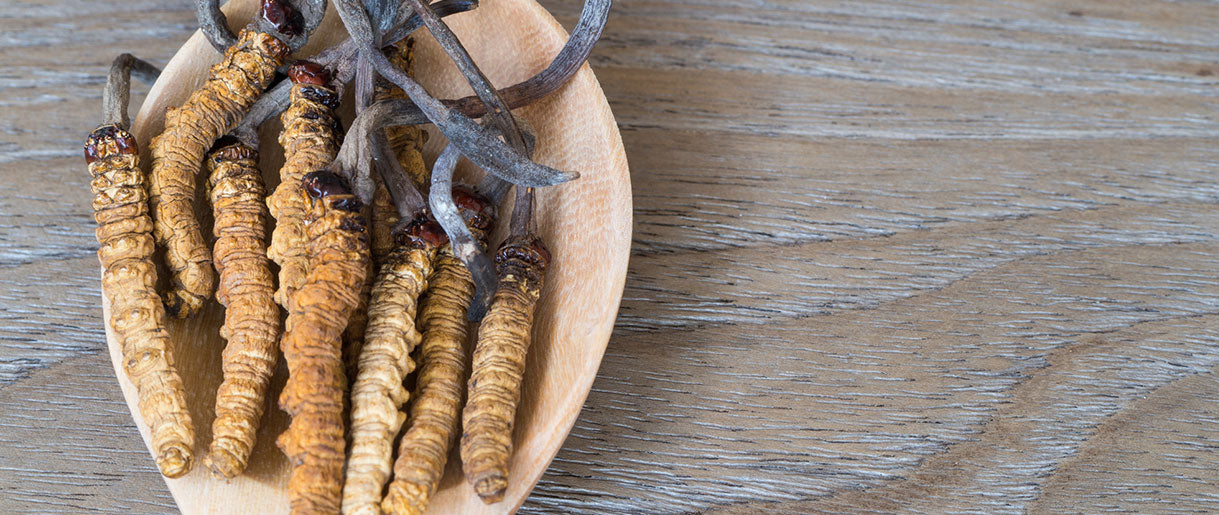
Benefits Of Cordyceps For Diabetes

Cordyceps mushroom is one of the healthiest fungi you can eat. As they have so many health benefits, the two most widely utilized species of these mushrooms, Cordyceps militaris and Cordyceps sinensis, have been employed not only in traditional Chinese medicine for millennia but also have been a subject of many studies. And according to scientific evidence, Cordyceps mushroom can help in the prevention and treatment of diabetes.
Several animal studies have shown promising results about the anti-diabetic effect of cordyceps mushrooms. For instance, scientists explored the anti-hyperglycemic activity of the fruiting body of Cordyceps in diabetic rats induced by nicotinamide and streptozotocin in a study from Taiwan(1).
Male Wistar rats were given either a placebo, the mushroom's fruiting body, carcass, or both carcass and fruiting body for four weeks. Then, on the 15th day, these rats were injected with the drugs.
Results of the study showed significant changes in blood sugar levels in the groups receiving the mushroom fruit body plus carcass and carcass alone. In addition, there was significantly lower weight gain and improved responses in the oral glucose tolerance test, which the administration of the fruit body of Cordyceps reduced.
Researchers concluded that the mushroom fruit body (not the carcass) attenuated weight loss induced by diabetes and hyperglycemia. The fruit body of Cordyceps has the potential to be a functional food in people with diabetes.
In another 2019 study(2) on streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice, the glucose-lowering properties of polysaccharides from Cordyceps were evaluated. The Kunming mice were injected with streptozotocin to induce diabetes, after which they were divided into five groups. Low, medium, and high doses of Cordyceps were given for 28 days, and the fasting sugar, insulin levels, and body weight were measured. Biopsies of the pancreatic tissue were also taken to evaluate the anti-diabetic effects.
Results showed that the anti-inflammatory effect of the mushroom was associated with its anti-diabetic effects. In addition, biopsies showed that the mushroom extract repaired and improved the damaged pancreatic tissue.
The mushroom exhibits anti-diabetic effects, and studies have shown the benefits of Cordyceps extract in treating diabetic kidney disease. Cordyceps(3) can tonify the kidney, and many Cordyceps sinensis-based Chinese patent medicines with high efficacy are frequently used to treat diabetic kidney disease.
Cordyceps militaris diabetes effects

A 2016 study(4) investigated the anti-diabetic effects of Cordyceps militaris extract in diabetic Sprague-Dawley rats induced by a feeding diet containing streptozotocin. For three weeks, half of the rats with diabetes mellitus caused by streptozotocin were given either a water extract or an alcohol extract of Cordyceps, while the other half, the control group, consumed the same diet without cordyceps.
Before and following Cordyceps treatment, researchers looked at the rats' body weights, blood glucose levels, lipid metabolism, and free radical levels. The mushroom also showed protective effects against nephropathy, a common renal complication in diabetes. In addition, cordyceps revealed inhibitory effects on blood markers of kidney involvement (such as urea nitrogen, protein, and uric acid).
The findings imply that Cordyceps possesses anti-diabetic capabilities and shields internal organs from harm caused by diabetes.
An oral glucose tolerance test analyzes the blood levels of insulin before and after consuming a sugary beverage. This test determines how well your body manages sugar by comparing the insulin secretion in various blood samples.
In diabetic rats receiving the cordyceps extract, the serum insulin level was much more stable than in the control group. Moreover, the cordyceps extracts stopped the blood sugar surge, particularly 60–120 minutes after consuming sugar.
To evaluate if Cordyceps militaris extracts can cause any harm, a histopathological analysis of diet-streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats and the control group was carried out.
These two groups' liver tissues did not significantly differ from one another, proving the safety of cordyceps. Furthermore, according to a study on kidney cells, the Cordyceps militaris extract shields the kidneys against damage brought on by streptozotocin.
Another similar study(5) evaluated the anti-diabetic and anti-nephritic effects of the Cordyceps militaris fruit body extracts on another group of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
The rats were continuously given Cordyceps orally for four weeks, along with the anti-diabetic medication metformin. In addition, each rat's body weight and fasting blood sugar were monitored.
Cordyceps showed hypoglycemic activity, indicated by a decrease in blood glucose. The kidney protective effects of the mushroom were confirmed by inhibitory effects on protein excretion in the urine (albuminuria) and blood levels of urea nitrogen and creatinine.
Fruiting body and mycelia have anti-diabetic effects

In another 2015 study(6), researchers evaluated the hypoglycemic activity of the fruiting body and mycelia of Cordyceps militaris in diabetic rats fed a high-fat diet. The fasting blood duster levels, oral glucose tolerance test, body weight, and blood biochemistry tests were measured.
Results showed that Cordyceps lowered blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity. Researchers concluded that the Himalayan mushroom possesses decisive hypoglycemia actions and could be an economical alternative diabetes treatment.
Cordyceps prevents male dysfunction

Oxidative testicular damage induced by diabetes is a global challenge. Cordycepin, the active compunction in Cordyceps mushrooms, is a natural antioxidant. In 2021(7), researchers investigated the protective effects of cordycepin against diabetes-induced testicular damage.
Streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice were treated with cordycepin for eight weeks. Results showed that cordycepin testicular damage and improved sperm function.
How Can You Take Cordyceps For Diabetes?

Extract from cordyceps is available as a powder or capsule. You can simply drink water with pills. You can drink powdered extract by dissolving it in a beverage.
While there is no exact Cordyceps sinensis diabetes dose, you can consume 1,000–3,000 mg daily in any form.
FAQs About Cordyceps Diabetes
Who Should Not Take Cordyceps?
If you have diabetes, cancer, a bleeding disease, or surgery planned in two weeks. You should avoid taking Cordyceps. Children and pregnant or nursing women should also steer clear of Cordyceps.
Can I Take Cordyceps Before Bed?
We recommend taking Cordyceps in the morning. Taking it right before the night is not advised as it may disrupt sleep.
Does Cordyceps Raise Blood Pressure?
Cordyceps does not raise blood pressure. Instead, studies have found that the mushroom extract may help stabilize blood pressure.
Key Takeaways
Diabetes mellitus is regarded as the world's third " killer " due to its significant morbidity and consequences. People are therefore looking for alternative anti-diabetic medications made from herbs or fungi.
Several animal studies have indicated Cordyceps diabetes effects and that the mushroom may help treat the condition. Talk to your healthcare provider if you want to try the mushroom.
References
- The anti-hyperglycemic activity of the fruiting body of Cordyceps in diabetic rats induced by nicotinamide and streptozotocin, (1)https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15050427/
- Glucose-lowering and hypolipidemic activities of polysaccharides from Cordyceps taii in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice, (2)https://bmccomplementmedtherapies.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12906-019-2646-x
- Mechanism of Cordyceps sinensis and its Extracts in the Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Review, (3)https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2022.881835/full
- Studies on the Antidiabetic Activities of Cordyceps militaris Extract in Diet-Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Sprague-Dawley Rats, (4)https://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmri/2014/160980/
- Antidiabetic and Antinephritic Activities of Aqueous Extract of Cordyceps militaris Fruit Body in Diet-Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Sprague Dawley Rats, (5)https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27274781/
- Hypoglycemic Activity through a Novel Combination of Fruiting Body and Mycelia of Cordyceps militaris in High-Fat Diet-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mice, (6)https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4519550/
- Cordycepin, a major bioactive component of Cordyceps militaris, ameliorates diabetes-induced testicular damage through the Sirt1/Foxo3a pathway, (7)https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34811786/








Let Us Know Your Comments